Introduction
Research
촉각기관의 모방 (Mimicking tactile organs)

촉각을 관장하는 4종류의 Mechanoreceptor (Merkel disk, Meissner Corpuscle, Ruffini ending, Pacinian Corpuscle)의 구조적 특징과 기능적 특징에서 착안하여, PZT 물질과 고분자 물질, 이온채널의 개념을 기반으로 인간의 촉각을 모사한 압력, 인장, 진동을 감지하는 다양한 센서에 대한 연구 및 개발.
Inspired by structural and functional properties of 4 kinds of mechanoreceptor (Merkel disk, Messiner Corpuscle, Ruffini ending, Pacinian Corpuscle) which are tactile organs, we study pressure, strain, vibration detective sensor based on PZT material, polymer, and Ion-channels.
인공청각센서 (Artificial Acoustic Sensors)

생명체의 청각기관이 소리를 듣는 방식을 모방하여 기존의 마이크로폰과 다른 차세대 음향 센서 기술을 개발한다.
동물의 달팽이관 내부에 존재하는 기저막은 소리의 주파수에 따라 서로 다른 위치에서 진동하는 얇은 막이다.
이러한 기저막의 진동 특성을 이용하여 특정 주파수 대역의 소리만을 선택적으로 감지할 수 있는 음향 센서를 제작한다.
또한 머신러닝을 활용하여 주파수 대역에 따라 나누어 감지된 소리 신호를 학습시켜 고성능 음성인식기술, 청각 보조장치, 공정 설비 감지 센서 등의 기술로 응용이 가능하다.
Mimicking the way living organisms hear sound, researchers are developing a next-generation acoustic sensor technology that differs from conventional microphones.
The basilar membrane, located inside the cochlea of animals, is a thin membrane that vibrates at different locations depending on the frequency of sound.
Utilizing the vibration characteristics of the basilar membrane, the we are fabricating acoustic sensors that can selectively detect sounds only within specific frequency bands.
Furthermore, by utilizing machine learning, the sound signals detected and divided according to the frequency band can be trained, enabling applications in technologies such as high-performance speech recognition, hearing aids, and facility detection sensors.
이온 채널 모사 에너지 소자 (Ion channel mimetic Energy device)

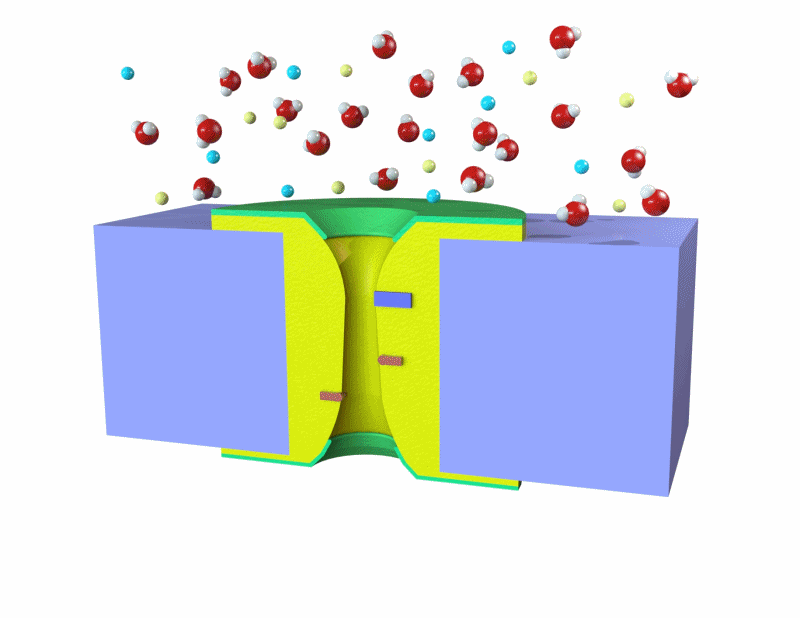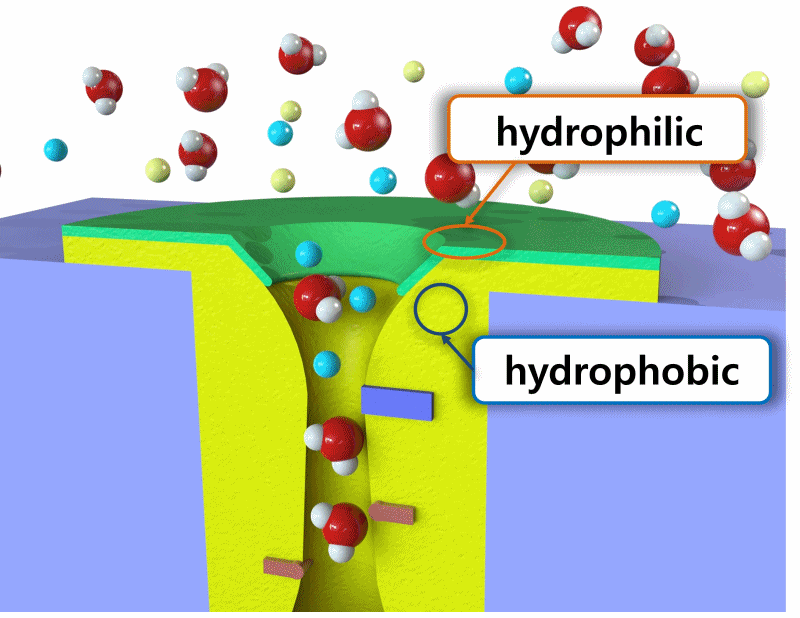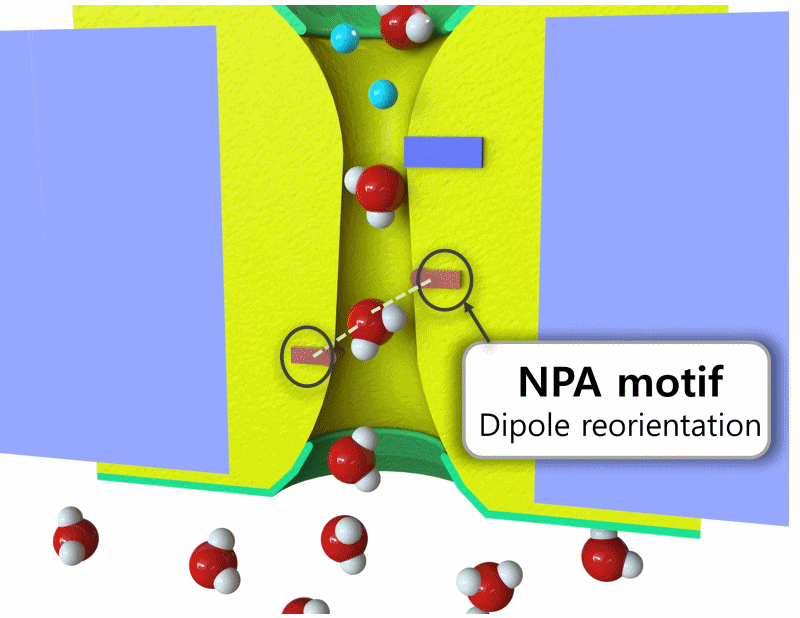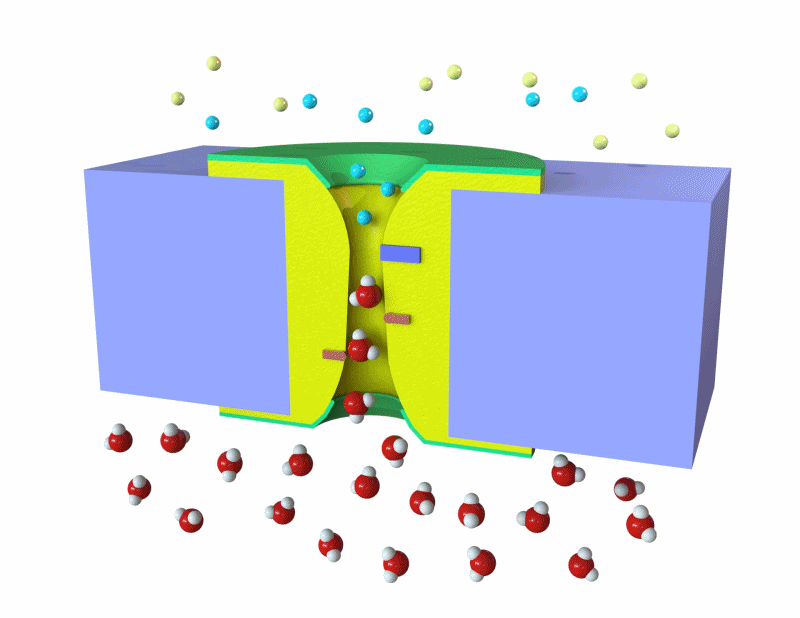
생체 세포는 K+ 및 Na+ 같은 이온을 선택적으로 막을 통과시켜 전기 신호를 생성하고, 이를 통해 전기적 전위 형성.
이러한 흥분성 세포와 이온 채널의 원리를 활용하여, 인체와 연동할 수 있는 친환경 에너지 소자를 개발 목표.
이온 농도 구배를 이용해 전기를 발생시키는 고성능의 에너지 소자와, 이온을 선택적으로 통과시킬 수 있는 이온 교환막의 기술을 개발. 사람의 몸과 결합하여 사용될 수 있는 에너지 소자로, 잠재적으로 의료기기나 웨어러블 기술에 적용이 가능한 기술 및 실용화를 목표로 함.
Biological cells generate bioelectric signals by selectively allowing ions like K+ and Na+ to pass through their membranes, thus forming an electrical potential. The goal is to develop eco-friendly energy devices that can interface with the human body, utilizing the principles of excitable cells and ion channels. The technology being developed includes high-performance energy devices that generate electricity using ion concentration gradients, and ion exchange membranes that selectively allow ions to pass. These devices, which can be integrated with the human body, have the potential to be applied in medical devices or wearable technologies, with a focus on practical application and technology commercialization.
마이크로/나노포어를 이용한 생체분자 검출 (Biomolecule sensing using micro/nanopore)

마이크로포어 기술은 마이크로 사이즈의 포어가 뚫린 멤브레인을 이용하여, 유체 내에서 흐르고 있는 생체 분자를 측정하고, 그것이 통과할 때 발생하는 전기적 신호를 분석하여 통과한 물질의 외부적 형상과 내부적 성질을 확인하는 기술이다. 여기서 얻어진 신호의 분석 및 다양한 특정 물질 센싱을 진행하고, 이를 기반으로 다른 여러 물질들이 동시에 존재하는 유체 내에서 특정 물질을 검출하고 이를 응용하여 암 진단 및 예후를 위한 액체 생검 플랫폼으로 발전될 수 있다.
Micropore Sensing is a technology that measures biomolecules flowing in a fluid using a membrane with perforated micro-sized pores and analyzes electrical signals generated when they pass to confirm the external shape and internal properties of the material. Here, the obtained signal analysis and various biomolecule sensing are performed, and based on the result, a specific biomolecule may be detected in a fluid in which various other substances are present at the same time and applied to develop a liquid biopsy platform for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
